Internal security
UPSC Syllabus for Internal security
Linkages between development and spread of extremism.
Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security.
Challenges to internal security through communication networks, role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cyber security; money-laundering and its prevention.
Security challenges and their management in border areas; linkages of organized crime with terrorism.
Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate.
2022
1) Discuss the types of organised crime. Describe the linkages between terrorists and organised crime that exist at the national and transnational levels. (150 words)
Organized crime refers to the activities of a group or network engaged in illegal enterprises that are coordinated and systematic in nature. Illegal activities carried out at a large scale for profit through organisation and planning by powerful criminal groups are known as organised crime.
Types of organized crimes:
Types of organized crimes:
- Drug Trafficking: This involves the production, transportation, and distribution of illegal drugs such as cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine etc.
- Human Trafficking: It includes activities such as sex trafficking, forced labour, and organ trafficking.
- Arms Trafficking: This involves the illegal trade and smuggling of firearms and ammunition
- Cybercrime: Illegal activities using digital platforms, including hacking, identity theft, financial fraud, and distribution of malware.
- Money Laundering: It is the process of concealing the origins of illegally obtained money.
- Financing of Terrorism: Organized crime groups provide financial support to terrorist organizations.
E.g.: At the international level, the Islamic State (IS) have collaborated with organized crime syndicates in Europe to smuggle fighters, weapons, and drugs into Europe. - Arms Procurement: Terrorist groups rely on organized crime networks for the procurement of weapons and ammunition.
- Logistical Support: Organized crime networks provide logistical support to terrorists, including safe houses, transportation, and forged documents.
E.g.: In J&K, counterfeit currency has been a major source of funding for terrorism.
2) What are the maritime security challenges in India? Discuss the organisational, technical and procedural initiatives taken to improve the maritime security. (150 words)
India faces several maritime security challenges due to its extensive coastline, strategic location, and maritime interests. These challenges pose a threat to the country’s economic and strategic interests, and can have a negative impact on the safety and security of shipping and the maritime environment.
Maritime security challenges in India:
Organizational
Maritime security challenges in India:
- Piracy and Maritime Terrorism: Pirates and terrorist groups target commercial ships, fishing vessels, and offshore installations and causing security concerns.
- Smuggling and Illicit Activities: Indian coast is susceptible drug trafficking, arms smuggling, and human trafficking.
E.g.: Seizure of narcotics shipments, such as heroin and synthetic drugs, by Indian Coast Guard in coastal regions. - Maritime Boundary Disputes: India has ongoing maritime boundary disputes with Pakistan over Sir Creek E.g.: Maritime dispute between India and Pakistan in the Sir Creek region has implications for security and resource exploitation.
- Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated Fishing (IUU): The presence of foreign fishing vessels engaged in IUU fishing affects India's maritime resources and coastal communities.
E.g.: The arrest of Sri Lankan fishermen in Indian waters for illegal fishing activities.
Organizational
- India launched security and growth for all (SAGAR) policy to integrated collaboration with Indian ocean region nations.
- National Committee for Strengthening Maritime and Coastal Security (NCSMCS): It reviews Coastal security periodically.
- Indian Coast Guard (ICG): The ICG is the primary agency responsible for maritime security in India
- Automatic Identification System (AIS): It enables maritime authorities to monitor vessel movements, track their positions, and identify potential security threats.
- Coastal Surveillance Network (CSN): It is a chain of static sensors having radars
- Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA): India has established a robust MDA system that integrates various surveillance technologies
E.g.: INS Arihant, INS Vikrant etc. - Interagency Coordination: Enhancing coordination among various agencies involved in maritime security is crucial.
E.g.: Post 26/11 – establishment of mechanism for inter-agency collaboration.
3) What are the different elements of Cyber security? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (250 words)
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage.
Elements of cyber security

Challenges in cyber security
Elements of cyber security
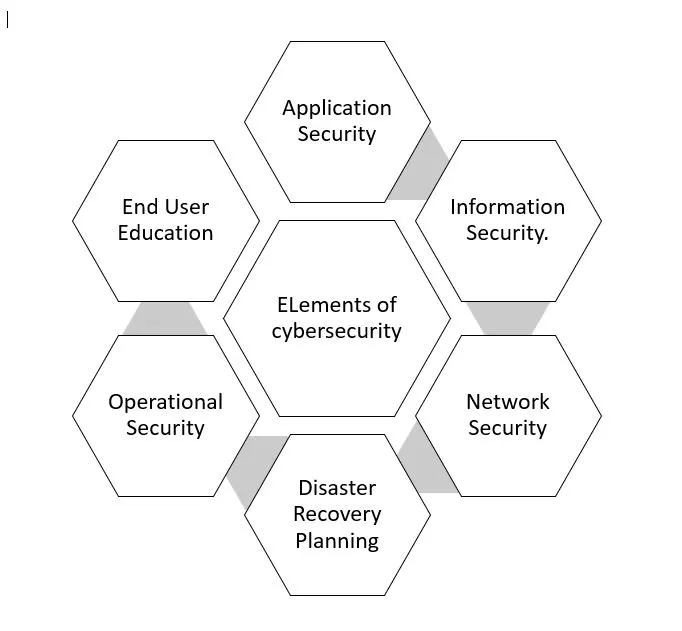
Challenges in cyber security
- Cyber terrorism: It is premeditated, politically motivated attack against information, computer systems, computer programs, and data which results in violence.
Eg.: Recently servers of All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) were targeted in a ransomware attack. - Digital Data Threat: Growing online transactions have generated bigger incentives for cybercriminals.
- Cyber warfare: It involves the actions by a nation-state or international organization to attack and attempt to damage another nation’s computers or information networks.
E.g.: Stuxnet – Destroying critical infrastructure. - Lack of specialists: Globally, India ranks 2nd in terms of the number of Internet users after China. However, India has a negligible base of cyber-security specialists, when compared to internet user base.
- National Cyber Security Policy, 2013: The policy provides the vision and strategic direction to protect the national cyberspace.
- The CERT-In (Cyber Emergency Response Team – India): CERT-In has been operational since 2004. It is the national nodal agency for responding to computer security incidents as and when they occur.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): The Union Government has decided to set up 14C. It will be apex coordination centre to deal with cybercrimes.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: Launched in early 2017, the Cyber Swachhta Kendra provides a platform for users to analyse and clean their systems of various viruses, bots/ malware, Trojans, etc.
- Difficult to track attacks from extra Territorial locations.
- Difficulty in International Coordination.
- India is not a member of the Budapest convention on cyber security.
- Lack of private sector participation in cyber security framework.
- Shortage of Skilled Professionals.
- IT Act 2002 and National Cyber Security Policy, 2013 are outdated and not well-equipped enough to handle technologically advanced cybercrimes.
- Lack of investments in emerging technology to handle cyber security incidents - Big Data, Al
4)Naxalism is a social, economic and developmental issue manifesting as a violent internal security threat. In this context, discuss the emerging issue and suggest a multi-layered strategy to tackle the menace of Naxalism. (250 words)
Naxalism is a violent form of left-wing extremism that is fuelled by issues such as social inequality, economic disparities, and political marginalization.
Social, economic and developmental issue manifesting Naxalism
Social, economic and developmental issue manifesting Naxalism
- Social Factors: Denial of dignity and untouchability, Poor implementation of laws -protection of civil rights and abolition of bonded labour etc.
- Economic: Disruption of traditional occupations and Rights, lack of alternative work opportunities.
E.g.: The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 deprives Tribals, who depend on forest produce for their living - Developmental: Dysfunctional Local governmental structures.
E.g.: Eviction and displacements by irrigation and power projects without adequate rehabilitation.
- Geographical Spread: Naxalism has expanded its reach to various states in India
- Evolving Tactics: Naxals groups employ propaganda, social media, and information warfare to spread their ideology and recruit new members.
- Nexus with Criminal Activities: Naxals groups engage in extortion, illegal mining, and drug trafficking to fund their operations
- Urban Naxalism: There have been instances of Naxals groups attempting to expand their influence into urban areas.
- Development and Governance: Improve infrastructure, healthcare, education, and livelihood opportunities. Strengthen local governance institutions, promote inclusive policies, and address issues of land rights and tribal welfare.
E.g.: ‘National Policy and Action Plan to address Left Wing Extremism’ - Security Measures: Specialized training, equipment, and infrastructure should be provided to security personnel deployed in Naxal-affected areas.
E.g: Setting up of Joint Task Forces for better inter-state coordination and intelligence sharing. - Community Engagement: Efforts should be made to bridge the gap between security forces and the local population through community policing initiatives and community outreach programs.
E.g.: Like Aspirational Districts Programme to improvement in governance and public perception management. - Rehabilitation and Reintegration: Initiating programs for the rehabilitation and reintegration of surrendered Naxals
- Counterinsurgency Operations: Conducting well-planned and intelligence-based counterinsurgency operations are necessary to disrupt the activities of Naxal groups.
E.g.: Operation Green Hunt – a massive deployment of security forces was done in the naxal-affected areas.
- Employment: Generating more employment and increase wages is important.
- Democratic method of conflict resolution.
- Rehabilitation and resettlement: Mining grounds, irrigation areas, industries, etc., in the area without any provision for the resettlement of the displaced people has only added to the woes of the poor.
- Remove disparity: Economic disparity and the growing distance between rich and the poor is one of the main problems that has contributed to the growth of Naxalism.
2021
5) How is S-400 air defence system technically superior to any other system presently available in the world? (150 words)
The S-400 air defence system, developed by Russia's Almaz-Antey, is considered one of the most advanced and capable air defence systems in the world
Technical superiority of S-400 Air defence system
Technical superiority of S-400 Air defence system
- Multiple Target Engagement: It can monitor and engage up to 80 targets at various altitude and speeds.
- Long-Range Coverage: Depending on the missile variant and target, it can identify and engage targets up to 400 kilometres. It has an edge over THAAD, in terms of range and hitting targets beyond the horizon.
- Advanced Tracking and Detection: It is equipped with advanced radar systems capable of detecting and tracking a wide range of targets, including stealth aircraft and hypersonic missiles.
- Diverse Missile Arsenal: It includes long-range and medium-range surface-to-air missiles, such as the 40N6, 48N6, and 9M96 series missiles.
- Deployment and speed: S-400 can be deployed in 5 mins, as compared to 25 minutes taken by Patriot. The highest speed of S-400 at 4.8 km/sec. surpasses Patriot’s 1.38 km/sec
- Countermeasures and Electronic Warfare Capabilities: It has the ability to jam or deceive enemy radars, enhancing its survivability and effectiveness in hostile environments.
6) Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (150 words)
Money laundering is disguising the identity of illegally obtained money so that it would appear to have originated from legitimate sources. Emerging technologies and globalization have both contributed to the complexity and scale of money laundering activities.
Emerging technologies contribute to money laundering:
National level
Emerging technologies contribute to money laundering:
- Crypto currencies: Digital currencies, such as Bitcoin, provide new avenues for money laundering due to their anonymous and decentralized nature
- Money launderers: It can transport illicit monies across jurisdictions through online payment systems and mobile banking platforms.
E.g.: Virtual currencies used in online gaming can also be used as a medium for money laundering - Cybercrimes: Hacking and cybercrime can be used to steal funds, alter transactions, and launder money.
E.g.: Phishing, malware attacks, and ransomware to gain unauthorized access to financial accounts and exploit them for money laundering purposes.
- Cross-Border Transactions and Trade: Globalization has facilitated increased cross-border trade, investments, and financial transactions.
- Tax evasion: The presence of offshore financial centres with lax regulations and banking secrecy laws has created opportunities for money launderers.
E.g.: Tax haven countries like Cayman Island, Panama etc. have structured their economies around assistance in tax evasion. - Offshore Financial Centres: Global trade networks may help to manipulate invoices and fictitious trades to move illicit funds
E.g.: Distribution of assets across countries prevents punitive action by authorities.
National level
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002: It criminalizes money laundering as a cognizable, non-bailable offence.
- Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND): It coordinates efforts of national and international intelligence, investigation and enforcement agencies against money laundering
- KYC Regulations: To verify customer identities and monitor transactions for suspicious activities.
- FATF: It sets standards and promotes effective implementation of legal, regulatory and operational measures against money laundering; terror financing
- Vienna Convention: Criminalize the laundering of money from drug trafficking
7) Keeping in view India’s internal security, analyse the impact of cross-border cyberattacks. Also discuss defensive measures against these sophisticated attacks. (150 words)
Cross-border cyberattacks have a profound impact on India's internal security, posing significant threats to various sectors and the nation as a whole. It makes the tracking of criminals difficult and cybersecurity a national security issue.
Impact of cross-border cyberattacks:
Impact of cross-border cyberattacks:
- Financial System Vulnerabilities: Attacks on financial systems can disrupt transactions, erode public trust, and harm investor confidence.
E.g.: Cosmos Bank Cyber Attack in Pune - Critical Infrastructure Disruption: These attacks can target critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, transportation, telecommunications, and defence and significantly impacts India's national security.
E.g.: attack on Oil India Ltd in 2022 - Data Breaches and Privacy Concerns: It aim to steal personal data, including financial information, social security numbers, and healthcare records.
E.g.: Attack UIDAI database 2018 - Social and Political Instability: These attacks targeting social media platforms to spread disinformation, manipulate public opinion, and sow social and political discord
- National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC):To coordinate with different agencies at the national level for cyber security matters
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In): To issue alerts and advisories regarding latest cyber threats
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: For detection of malicious programs
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC): To deal with cyber security issues
8) Analyse the multi-dimensional challenges posed by external state and non-state actors, to the internal security of India. Also discuss measures required to be taken to combat these threats. (250 words)
India faces multiple external security threats from both state and non-state actors. These threats have various dimensions and pose significant challenges to India's internal security.
Challenges posed by external state and non-state actors
Challenges posed by external state and non-state actors
- Border Security: External state actors and non-state actors can exploit India’s vulnerabilities to carry out attacks, promote separatist movements, or engage in transnational crimes.
- Terrorism: Terrorist groups operating from across the border, such as Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) and Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), pose a significant threat.
- Insurgency and Naxalism: Domestic insurgent groups in North-eastern regions such as ULFA and Naxalite movements in Red corridor pose serious threats.
- Cyber-threats: The increasing reliance on digital infrastructure makes India susceptible to cyberattacks from state-sponsored entities and non-state actors
- Money laundering: Indulging in counterfeit currency and money laundering activities and providing illegal funds to insurgents in NE India
- Drug trafficking: It is a serious threat due to proximity to golden crescent and golden triangle routes.
- Enhancing border infrastructure by deploying modern surveillance systems
- Enhance cooperation with international partners in intelligence sharing
- Develop robust cybersecurity frameworks
- Enhance intelligence gathering and analysis capabilities by leveraging technologies such as AI, data analytics
- Implement development programs in insurgency-affected areas.
9) Analyse the complexity and intensity of terrorism, its causes, linkages and obnoxious nexus. Also suggest measures required to be taken to eradicate the menace of terrorism. (250 words)
Terrorism has diverse causes, including political, ideological, social, economic, and religious factors. Grievances arising from perceived injustice, political marginalization, ethnic or religious tensions, poverty, unemployment, and ideological indoctrination can contribute to the growth of terrorism.
Complexity and intensity of terrorism
Complexity and intensity of terrorism
- Motivations and Ideologies: Terrorism can stem from diverse motivations and ideologies, ranging from religious extremism to separatism, nationalism, or socio-political grievances
- Global Reach: Terrorism has the potential to transcend borders and affect multiple regions worldwide. The global reach of some terrorist groups adds to the complexity and intensity of the threat they pose.
- Tactics and Technology: Terrorist groups adapt their tactics and exploit advancements in technology, such as the use of social media for propaganda, remote communication, and coordination. This can increase the intensity and global impact of their activities.
- State Sponsorship: Some terrorist organizations receive support from state actors, either directly or indirectly. State sponsorship can enhance the intensity of terrorist activities and make it more difficult to combat.
- Political Grievances: Perceived political injustices, marginalization, and lack of representation can lead individuals or groups to resort to terrorism to advance their agendas or demand political change.
- Religious Extremism: Radical interpretations of religious beliefs can motivate individuals to carry out acts of violence in the name of their faith, leading to religious terrorism.
- Ethnic or Nationalistic Goals: Ethnic or nationalist movements seeking autonomy or independence may resort to terrorism as a means to achieve their objectives.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, unemployment, and economic disparities can create an environment of frustration and hopelessness, pushing some individuals toward terrorism as a way to vent their grievances.
- Ideological Affiliations: Some terrorist groups share common ideologies and objectives, leading to cooperation, resource sharing, and training among them.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: Terrorist organizations may form alliances or cooperate across national borders to enhance their capabilities and evade counter-terrorism efforts.
- Financing and Funding Networks: There can be interconnected financial networks that provide funding and resources to multiple terrorist groups, enabling their activities.
- Organized Crime and Terrorism: In some cases, terrorist groups collaborate with organized crime networks to fund their operations through illegal activities such as drug trafficking, arms smuggling, or human trafficking.
- Corruption and Terrorism: Corruption within governments or security forces can enable terrorists to operate with impunity or obtain sensitive information and support.
- Cyber terrorism and Technology: Terrorist groups may exploit the internet and technology for propaganda, recruitment, and cyber-attacks.
- Intelligence Cooperation: Strengthen international intelligence sharing and cooperation
- Effective Border Controls: Implement robust border controls, including advanced technology and intelligence-based screening
- Countering Radicalization and Extremism: Promotes inclusive societies and addresses social and economic disparities.
- Disrupting Financing: Targeting the financial infrastructure of terrorist organizations and cutting off their funding sources
- International Norms and Cooperation: Strengthen international norms and legal frameworks against terrorism
- Countering Online Radicalization: Combat the spread of terrorist propaganda and recruitment through the internet and social media platforms
2020
10) Discuss different types of cybercrimes and measures required to be taken to fight the menace. (150 words)
Cybercrime refers to criminal activities that are carried out using digital devices or the internet.
Different types of cybercrimes
Different types of cybercrimes
- Hacking: Unauthorized access to computer systems or networks for the purpose of stealing or manipulating data.
- Phishing: A fraudulent attempt to obtain sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details, by disguising oneself as a trustworthy entity.
- Malware: Malicious software that is designed to damage or disrupt computer systems, steal data or control systems.
- Identity theft: Theft of personal information, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and bank account details, for fraudulent purposes.
- Cyberstalking: Harassment or stalking of individuals using digital devices or the internet.
- Awareness campaigns: Raise public awareness about cyber threats and the risks associated with online activities
- Stronger cybersecurity: Organizations and individuals need to implement stronger cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
- International cooperation: International cooperation among law enforcement agencies is essential to combat it.
- Legal framework: Strong legal frameworks and harsher punishments for cybercriminals can deter potential offenders and improve cybercrime prevention.
11) For effective border area management, discuss the steps required to be taken to deny local support to militants and also suggest ways to manage favourable perception among locals. (150 words)
Effective border area management requires a multi-pronged approach to prevent local support to militants and manage favourable perception among locals.
Steps required for effective border area management
Steps required for effective border area management
- Strengthening border security: Effective border security measures, such as border fencing, surveillance, and patrolling, can prevent militants from entering or exiting the country and disrupting local communities.
- Community engagement: Engaging with local communities and building trust through dialogue and cooperation
- Economic development: Promoting economic development and providing job opportunities to locals can reduce their vulnerability to exploitation by militants.
- Countering propaganda: Counter-propaganda measures, such as awareness campaigns and media outreach, can help to counter the false narratives of militants and deny their support
- Effective governance: Providing efficient and transparent governance, addressing local grievances, and ensuring the delivery of public services.
- Community development: Investing in community development projects, such as schools, hospitals, and roads
- Cultural sensitivity: Respecting local cultures, traditions, and customs reduces the risk of alienation and resentment.
- Dialogue and cooperation: Engaging with local leaders and communities in a respectful and constructive manner
12) What are the determinants of left-wing extremism in Eastern part of India? What strategy should Government of India, civil administration and security forces adopt to counter the threat in the affected areas? (250 words)
The left-wing extremism (LWE) in India started with uprising in Naxalbari, West Bengal by the Communist Party of India (Marxist).
Determinants of left-wing extremism in Eastern part of India
Determinants of left-wing extremism in Eastern part of India
- Socio-economic Inequalities: Deep-rooted socio-economic inequalities, including land ownership, access to resources, and basic services, have created grievances among marginalized communities.
- Tribal Issues: Issues related to land rights, displacement, and exploitation, has provided fertile ground for LWE groups to propagate their ideology and garner support.
- Governance Deficit: Weak governance, corruption, and the absence of effective administration in remote and tribal areas have led to a lack of trust in government institutions.
- Development Initiatives: Provide access to education, healthcare, infrastructure, and livelihood opportunities in LWE-affected areas.
- Strengthening Governance: Enhance the capacity of local administration and governance structures, improve service delivery, and address corruption and grievances
- Security Measures: Deploying well-trained and adequately equipped security forces to effectively counter LWE violence
- Community Engagement: Encouraging community participation and creating awareness about the ill-effects of LWE ideologies
- Intelligence and Coordination: Strengthening intelligence gathering and sharing mechanisms among various security agencies
13) Analyse internal security threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (250 words)
Internal security threats and transborder crimes along the borders of Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Pakistan, including the Line of Control (LoC), pose significant challenges to India's security.
Internal security threats and transborder crimes along the borders
Role of Various Security Forces
Internal security threats and transborder crimes along the borders
| India-Myanmar | India-Bangladesh | India-Pakistan |
|
|
|
- Indian Army: They conduct regular patrols, search and destroy operations, intelligence gathering, and maintain a strong presence to prevent infiltration and maintain law and order.
- Border Security Force (BSF): BSF is responsible for securing the land borders with Bangladesh and Pakistan. They carry out border patrolling, surveillance, and intercept illegal activities, including smuggling, infiltration, and transborder crimes.
- Assam Rifles: Assam Rifles is deployed along the Myanmar border and actively participates in counter-insurgency operations, border management, and development activities in the region.
- State Police Forces: State police forces play a crucial role in maintaining law and order, intelligence gathering, and supporting the central security forces in dealing with internal security threats along the borders.
2019
14) The banning of ‘Jamaat-e – islaami’ in Jammu and Kashmir brought into focus the role of over-ground workers (OGWs) in assisting terrorist organizations. Examine the role played by OGWs in assisting terrorist organizations in insurgency affected areas. Discuss measures to neutralize influence of OGWs. (150 words)
Over-ground workers (OGWs) are individuals who are not directly involved in carrying out acts of terrorism but provide logistical, financial, and ideological support to terrorist groups.
Role of OGWs in assisting terrorist organizations
Role of OGWs in assisting terrorist organizations
- Logistics and Support: OGWs assist in providing logistical support to terrorists, including safe houses, transportation, and hideouts. They help in maintaining communication networks, arranging meetings, and facilitating the movement of terrorists.
- Intelligence and Surveillance: OGWs gather information about security forces, local infrastructure, and vulnerable targets for terrorist attacks.
- Recruitment and Radicalization: OGWs are involved in identifying and recruiting new members into terrorist organizations. They facilitate the process of radicalization by disseminating extremist propaganda and conducting ideological indoctrination
- Financial Assistance: OGWs assist in fundraising activities by collecting and channelling funds to support terrorist organizations.
- Strengthen intelligence networks and improving coordination between security agencies
- Building trust and cooperation between security forces and local communities is essential.
- Conducting targeted operations to apprehend OGWs and disrupt their activities is crucial.
- Strengthen legal frameworks and ensuring effective prosecution of OGWs
- Deradicalization, skill development, and psychological counselling measures are needed
15) What is CyberDome Project? Explain how it can be useful in controlling internet crimes in India. (150 words)
The CyberDome Project is an initiative undertaken by the Kerala Police in India to combat cybercrimes and enhance cybersecurity. It is a state-of-the-art facility that focuses on proactive measures, technological advancements, and capacity building to address the challenges posed by cyber threats. It aims to create a secure cyber ecosystem and provide a safe digital environment for individuals, businesses, and organizations.
Use of CyberDome Project in controlling internet crimes
Use of CyberDome Project in controlling internet crimes
- Technology and Expertise: The CyberDome Project is equipped with advanced technologies, tools, and software to detect, prevent, and investigate cybercrimes. It employs skilled professionals who are trained in cyber forensics, data analysis, and digital investigations.
- Proactive Approach: It focuses on preventive measures, including continuous monitoring, threat intelligence, and vulnerability assessments.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: It facilitates the sharing of information, best practices, and intelligence to collectively combat cybercrimes.
- Awareness and Education: It conducts awareness programs, workshops, and training sessions to educate individuals, businesses, and organizations about cybersecurity best practices.
- Incident Response and Support: It offers guidance, counselling, and technical assistance to individuals and organizations affected by cyberattacks
- Research and Innovation: It encourages research and innovation in the field of cybersecurity.
16) Indian government has recently strengthened the anti-terrorism laws by amending the unlawful activities (Prevention) act (UAPA), 1967 and the NIA Act. Analyse the changes in the context of prevailing security environment while discussing the scope and reasons for opposing the UAPA by human rights organizations. (250 words)
The UAPA Amendment Act, 2019 and The NIA (Amendment) Act 2019 has aims to strengthen the anti-terrorism laws.
Changes in the UAPA and NIA Act
Changes in the UAPA and NIA Act
- The amendments expanded the definition of terrorism
- The amendments grant the government the power to designate individuals as terrorists, including Indian citizens
- The amendments allow for an extension of the investigation period from 90 days to 180 days
- The amendments confer additional powers to investigate offenses committed outside India
- Overreach and Abuse: Critics argue that the broad definition of terrorism and the power to designate individuals as terrorists may be misused or arbitrarily applied, leading to harassment or curtailment of rights of individuals.
- Lack of Safeguards: Critics argue that the amendments should have included provisions to ensure proper oversight, accountability, and judicial scrutiny to prevent potential abuse of power.
- Curtailment of Due Process: Concerns have been raised about the extension of the investigation period and its impact on the principle of timely justice.
- Impact on Freedom of Expression: Critics argues that the broadening of the definition of terrorism may impinge on freedom of expression and dissenting voices, potentially curbing democratic rights and stifling legitimate activism.
17) Cross-border movement of insurgents is only one of the several security challenges facing the policing of the border in North-East India. Examine the various challenges currently emanating across the India-Myanmar border. Also discuss the steps to counter the challenges. (250 words)
The India-Myanmar border is a critical area of concern for India's national security due to the presence of insurgent groups and other transnational criminal networks. border in North-East India facing several security threats such as Ethnic and Tribal Tensions, Insurgency and Militancy, Arms Smuggling and Proliferation, Narcotics and Human Trafficking etc.
Challenges in India-Myanmar border
Challenges in India-Myanmar border
- Insurgency and Armed Groups: The presence of various insurgent groups including National Socialist Council of Nagaland-Khaplang (NSCN-K), United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA), and Manipur-based outfits.
- Illegal Cross-Border Activities: Illegal activities, including smuggling of goods, human trafficking, and circulation of counterfeit currency are common.
- Porous Border: The absence of physical barriers, inadequate fencing, and limited patrolling resources contribute to the porosity of the border, enabling unauthorized movements.
- Ethnic and Tribal Tensions: The border region is home to diverse ethnic communities and tribes with varying social, cultural, and political aspirations.
- Strengthening Border Infrastructure: Improve border infrastructure, including the construction of roads, bridges, and border outposts
- Border Management and Coordination: Effective coordination of Border Security Force (BSF) and Assam Rifles is crucial
- Enhanced Surveillance and Technological Solutions: Deploy high-resolution cameras, thermal imaging devices, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Strengthening Intelligence Mechanisms: Strengthen intelligence networks, increase human intelligence sources, and integrating intelligence agencies
- Bilateral Cooperation: Collaborative efforts with Myanmar authorities are crucial
2018
18) The China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is viewed as a cardinal subset of China’s larger ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative. Give a brief description of CPEC and enumerate the reasons why India has distanced itself from the same. (150 Words)
The China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a significant infrastructure development project that aims to connect China's north western region of Xinjiang to Pakistan's Gwadar Port in the Arabian Sea. It is considered a crucial part of China's broader "One Belt One Road" (OBOR) initiative. CPEC involves a network of highways, railways, pipelines, and energy projects, with a focus on improving connectivity and trade between China and Pakistan
Reasons why India has distanced itself from the CPEC
Reasons why India has distanced itself from the CPEC
- Sovereignty and Territorial Concerns: The CPEC route via Gilgit-Baltistan, which India claims as part of Jammu and Kashmir, is a major concern for India.
- Security and Strategic Concerns: India has raised concerns about the strategic implications of CPEC, as it enhances China's presence and influence in Pakistan.
- Lack of Transparency and Consultation: India has criticized the lack of transparency and consultation in the planning and implementation of CPEC.
- China's Support for Pakistan: India perceives China's close partnership with Pakistan, including its significant financial and infrastructural support through CPEC, as a challenge to its own regional influence.
- Bilateral Disputes: India and Pakistan have a long-standing history of bilateral disputes, including territorial and security issues.
19) Left Wing Extremism (LWE) is showing a downward trend, but still affects many parts of the country. Briefly explain the Government of India’s approach to counter the challenges posed by LWE. (150 Words)
According of ministry of home affairs data, the incidents of Naxal violence in the country have dropped by 77 % between 2009 and 2021, and deaths of security force personnel due to Maoist violence have more than doubled in Chhattisgarh in the past three years.

Government of India’s approach to counter the challenges posed by LWE
Government of India’s approach to counter the challenges posed by LWE
- Security operations: The government has deployed security forces to conduct anti-LWE operations in affected areas, with a focus on neutralizing the top leadership of LWE groups.
- Development initiatives: The government has launched several development initiatives in LWE-affected areas, including infrastructure development, employment generation, and provision of basic amenities like healthcare and education.
- Rehabilitation and Surrender Policy: The government has formulated policies to encourage LWE cadres to surrender and join the mainstream, providing them with rehabilitation and reintegration support.
- Capacity Building: The government focuses on building the capacity of state police forces to effectively combat LWE.
- Intelligence and Coordination: The government emphasizes intelligence gathering and sharing to disrupt LWE networks and prevent attacks.
20) Data security has assumed significant importance in the digitized world due to rising cyber-crimes. The Justice B. N. Srikrishna Committee Report addresses issues related to data security. What, in your view, are the strengths and weaknesses of the Report relating to protection of personal data in cyber space? (250 Words)
The Justice B. N. Srikrishna Committee Report is a comprehensive document that addresses issues related to data security and the protection of personal data in cyberspace.
Importance of data security in the digitized world
Importance of data security in the digitized world
- Increased Sophistication of Cyber-Criminals: Cyber-criminals are becoming more sophisticated and organized in their approach. They use advanced techniques, such as malware, ransom ware, phishing, and social engineering, to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
- Impact on Individuals and Organizations: Data breaches can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations.
- Global Connectivity: The interconnectedness of the global economy and the internet means that a cyber-attack on one part of the world can have far-reaching consequences.
- Financial Motivation: Cyber-crimes are often financially motivated. Criminals may steal personal information to commit identity theft, engage in financial fraud, or sell stolen data on the dark web.
- Comprehensive approach: The report covers various aspects such as consent, purpose limitation, data localization, accountability, and individual rights.
- Privacy-centric approach: The report emphasizes the importance of privacy as a fundamental right and recommends the establishment of a data protection authority and the implementation of privacy-enhancing measures.
- Strong Legal Foundation: The research suggests passing the Personal Data Protection Bill to establish a legal foundation for data protection in India.
- Balancing innovation and regulation: While the report aims to enhance data protection, some critics argue that it may impose stringent regulations that could stifle innovation and hinder the growth of the digital economy.
- Data localization provisions: While data localization measures aim to enhance data security and facilitate law enforcement, they also create barriers to global data flows and have economic implications for multinational companies.
- Regulatory oversight challenges: The establishment of a data protection authority, as recommended by the report, raises questions about its structure, independence, and effectiveness.
21) India’s proximity to two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What countermeasures should be taken to prevent the same? (250 Words)
India's proximity to two major illicit opium-growing states, namely Afghanistan and Myanmar, has indeed raised internal security concerns. Drug trafficking is often linked to various other illicit activities.
Linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities
Linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities
- Drug Trafficking and Gunrunning: Drug trafficking networks often engage in gunrunning to protect their illicit operations and defend their territories. The profits generated from drug trafficking are used to acquire weapons and ammunition.
- Drug Trafficking and Money Laundering: Drug trafficking generates substantial profits that need to be laundered to legitimize the illicit funds.
- Drug Trafficking and Human Trafficking: Drug trafficking networks often exploit vulnerable individuals, including women and children, for transporting drugs.
- Strengthening law enforcement: Enhancing the capacity and capabilities of law enforcement agencies to investigate and dismantle drug trafficking networks.
- International cooperation: Sharing intelligence, conducting joint operations, and extraditing criminals involved in cross-border crimes.
- Public awareness and education: Conducting awareness campaigns to educate the public about the dangers of drug abuse and the interlinkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities.
- Strengthening legal frameworks: Enacting and enforcing comprehensive legislation to address drug trafficking, money laundering, human trafficking, and related offenses.
2017
22) Discus the potential threats of Cyber-attack and the security framework to prevent it. (150 words)
A cyber-attack refers to an intentional, malicious attempt to compromise the security of computer systems, networks, devices, or data using various techniques and methods. Cyber-attacks pose significant threats to individuals, organizations, and nations.
Threats of cyber attacks
Threats of cyber attacks
- Malware: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware, can infect computers and networks, causing damage, data theft, or unauthorized access.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Cybercriminals use deceptive techniques to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details, through phishing emails, fake websites, or impersonation.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: Attackers overwhelm a target system with a flood of requests, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Sophisticated attackers infiltrate networks and remain undetected for long periods, stealing sensitive information
- Risk Assessment and Management: Organizations should conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats
- Access Controls and Authentication: Implementing strong access controls, including multifactor authentication and role-based access, helps ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive systems and data.
- Network Security: Deploying firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and secure configurations helps protect networks from unauthorized access and detects potential intrusions.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access or interception.
23) The North-East region of India has been infested with insurgency for a very long time. Analyse the major reasons for the survival of armed insurgency in this region. (150 words)
The North-East region of India has indeed witnessed persistent armed insurgency by United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA), National Socialist Council of Nagaland (NSCN) and National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) for a significant period.
Major reasons for the survival of armed insurgency in the North-East region
Major reasons for the survival of armed insurgency in the North-East region
- Historical Factors: Historical grievances, perceived marginalization, and unresolved issues related to land rights, ethnic tensions, and migration have fuelled the insurgent movements.
- Socio-Economic Factors: Inadequate infrastructure, limited access to education and healthcare, unemployment, and poverty creates a fertile ground for recruitment and support for insurgent groups.
- Border Issues: Weak border management and infiltration contribute to the survival of insurgent movements.
- Arms Availability Arms trafficking networks and porous borders facilitate the inflow of weapons to sustain the armed movements.
- External Support: Insurgent groups in the North-East have, at times, received external support, including training, arms, and safe havens, from neighbouring countries.
- Lack of Political Dialogue: The absence of sustained and inclusive political dialogue between the government and insurgent groups has hindered conflict resolution.
- Limited State Capacity: The region's geographical terrain, with dense forests, hilly terrains, and riverine systems, poses challenges to security operations.
- Enhance communication and connectivity, infrastructure improvement for better integration of the region with the mainland.
- Stringent law and fast criminal justice system for quick disposal of insurgents attack cases.
- Greater coordination between central forces and state forces for better tactical response.
- Greater cultural interaction with the rest of the country and socio-economic development that includes a holistic inclusive development.
- Decentralization with alertness, Improving administrative efficiency, pro-people governance and coping up with regional aspirations
24) Mob violence in emerging as a serious law and order problem in India. By giving suitable example, analyse the causes and consequences of such violence. (250 words)
Mob lynching is a term used to describe the acts of targeted violence by a large group of people. The violence is tantamount to offences against human body or property- both public as well as private. Mob violence has indeed emerged as a serious law and order problem in India.
Causes of mob violence
Causes of mob violence
- Rumours and Misinformation: In many cases, mob lynching incidents are triggered by rumours or false information circulated through social media or word of mouth.
E.g.: Dhule Lynching Case - Deep-Rooted Prejudices: Mob lynching is often driven by deep-rooted prejudices and biases based on religion, caste, or communal affiliations.
E.g.: Mohammed Akhlaq lynching case - Failure of Law Enforcement: Weak law enforcement and delayed justice can create an environment where individuals take the law into their own hands
E.g.: Dimapur Mob Lynching case
- Loss of Life and Dignity: The primary consequence of mob lynching is the loss of innocent lives and the violation of human dignity
- Social Divisions and Polarization: It deepens mistrust, fear, and animosity between different groups, hindering social harmony and integration.
- Erosion of Rule of Law: Mob lynching undermines the rule of law and weakens trust in the justice system.
- Fear and Intimidation: Mob lynching creates an atmosphere of fear and intimidation within society.
25) The scourge of terrorism is a grave challenge to national security. What solutions do you suggest to curb this growing menace? What are the major sources of terrorist funding? (250 words)
Terrorism is a global problem and India is no exception to it. It poses a grave challenge to national security and has resulted in loss of precious lives and property.
The scourge of terrorism is a grave challenge to national security
The scourge of terrorism is a grave challenge to national security
- Loss of Lives and Human Tragedy: Terrorist attacks often result in the loss of innocent lives and cause immense human suffering.
- Economic Impact: Terrorist attacks can have severe economic consequences. They can damage critical infrastructure, deter foreign investments, and disrupt trade and business activities, leading to economic losses.
- Border Security Concerns: Terrorist groups often exploit porous borders and weak border security measures to move personnel, funds, and weapons across international boundaries.
- Destabilization of Society: Terrorism seeks to disrupt the normal functioning of society and create an atmosphere of instability, making it difficult for governments to provide essential services and maintain law and order.
- Damage to National Reputation: Repeated terrorist attacks can tarnish a nation's reputation internationally, impacting diplomatic relations and tourism.
- Coordination among security agencies: Effective coordination among intelligence and security agencies is crucial to tackle terrorism.
- Stronger laws: The existing laws should be strengthened to deal with terrorism. The laws should be more stringent and have a deterrent effect on the perpetrators of terrorism.
- International cooperation: Terrorism is a global problem and requires international cooperation. India should work with other countries to prevent terrorist activities.
- Addressing root causes: The root causes of terrorism such as poverty, unemployment, and social inequality should be addressed. Developmental programs should be implemented to provide opportunities to the marginalized sections of the society.
- Criminal activities: Terrorist groups often engage in criminal activities such as drug trafficking, arms smuggling, and extortion to generate funds.
- Donations: Terrorist groups receive donations from sympathizers and supporters.
- State sponsorship: Some states provide financial support to terrorist groups for geopolitical reasons.
- Money laundering: Terrorist groups also engage in money laundering to conceal the sources of their funds.
2016
26) The terms ‘Hot Pursuit’ and ‘Surgical Strikes’ are often used in connection with armed action against terrorist attacks. Discuss the strategic impact of such actions. (200 words)
"Hot Pursuit" and "Surgical Strikes" are terms commonly associated with military responses to terrorist attacks.
Strategic impacts of "Hot Pursuit" and "Surgical Strikes"
Strategic impacts of "Hot Pursuit" and "Surgical Strikes"
- Deterrence: Hot Pursuit and Surgical Strikes send a strong message to terrorist groups and their supporters that their actions will not go unanswered. By swiftly and decisively targeting terrorists, armed forces demonstrate their resolve to protect national security and deter future attacks.
- Preventive Action: Hot Pursuit and Surgical Strikes are often carried out to pre-empt terrorist activities and prevent them from executing their plans. By proactively targeting terrorist hideouts, training camps, or individuals involved in planning attacks, security forces aim to neutralize threats before they can materialize.
- Psychological Impact: These actions can have a profound psychological impact on both terrorists and the general population. For terrorists, it undermines their sense of invincibility and exposes their vulnerability.
- International Signalling: Hot Pursuit and Surgical Strikes also serve as a means of international signalling. They demonstrate a nation's determination to combat terrorism and protect its sovereignty.
- Retaliation and Justice: In some cases, Hot Pursuit and Surgical Strikes are carried out in response to specific terrorist attacks or incidents. They provide a means for retaliation and seeking justice for the victims.
27) ‘Terrorism is emerging as a competitive industry over the last few decades.” Analyse the above statement. (200 words)
terrorism has become a lucrative business for certain groups, rather than a mere means to achieve political or ideological goals. In recent years, there has been an increase in the frequency and severity of terrorist attacks around the world, and this has been driven in part by the growing availability of funding and resources for terrorist groups.
Terrorism is emerging as a competitive industry over the last few decades
Terrorism is emerging as a competitive industry over the last few decades
- Diverse and Proliferating Actors: there has been a proliferation of diverse actors, including non-state groups, lone-wolf attackers, and self-radicalized individuals. These actors often compete with each other for attention and influence, leading to a fragmented and decentralized terrorist landscape.
- Use of Modern Communication Technologies: Advancements in communication technologies, particularly the internet and social media, have allowed terrorist groups and individuals to disseminate propaganda, recruit followers, and coordinate attacks on a global scale.
- Ideological and Strategic Competition: Different terrorist groups may have differing ideological or strategic objectives, leading to competition among them for resources, territorial control, and media attention.
- Attention-Seeking and Notoriety: Terrorism thrives on creating fear and drawing attention to its cause. As groups compete for media coverage and public attention, they may resort to more spectacular and brutal acts of violence to make their presence felt.
- Copycat Attacks and Inspiration: The success of one terrorist attack can inspire others to emulate or replicate similar acts of violence.
- Exploiting Conflicts and Weak Governance: Terrorist groups capitalize on existing conflicts, political instability, and weak governance in certain regions, further fuelling the competitive nature of terrorism as various groups vie for control and influence.
- Strong Intelligence and Surveillance: Strengthen intelligence gathering and analysis capabilities to identify and pre-empt terrorist threats. Improve coordination among intelligence agencies and enhance surveillance of potential targets.
- Effective Border Management: Strengthen border security and enhance surveillance along India's borders to prevent the infiltration of terrorists and illegal activities.
- Community Engagement and Outreach: Engage with local communities to build trust and cooperation. Encourage community members to report suspicious activities and involve them in countering violent extremism efforts.
- Counter-Radicalization Programs: Implement programs to counter radicalization and extremism, promoting a message of peace, tolerance, and inclusivity. Collaborate with civil society organizations, religious leaders, and community influencers in this endeavour.
- Addressing Root Causes: Tackle the root causes of terrorism, such as socio-economic disparities, political grievances, and communal tensions. Promote inclusive development and ensure that grievances are addressed through peaceful and democratic means.
28) Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. (200 words)
Borders are the lines which separate the territories of two or more sovereign nations. India has a land border of over 15,000 kms, which it shares with seven countries (Pakistan, China, Bangladesh, Nepal, Myanmar, Bhutan, and Afghanistan).
Challenges in Border Management
Challenges in Border Management
- Geographical and Territorial Challenges: Borders often traverse difficult terrains, such as mountains, deserts, forests, or rivers, making physical surveillance and control challenging.
- Porous Borders and Illicit Activities: Porous borders facilitate the movement of unauthorized individuals, smuggling of contraband goods, illegal migration, and cross-border terrorism.
- Hostile Relations: Border management becomes more challenging when there are hostile relations or unresolved conflicts with neighbouring countries.
- Limited Resources: Budgetary constraints, competing priorities, and vast border lengths often limit the availability of necessary resources.
- Border Infrastructure Development: Constructing and maintaining appropriate border infrastructure, including border fencing, checkpoints, roads, and border outposts, can help manage movement across borders effectively.
- Intelligence and Information Sharing: Developing robust intelligence networks and promoting information sharing among agencies is essential.
- Bilateral and Regional Cooperation: Establishing communication channels, joint patrolling, and sharing best practices can help address common challenges and build trust.
- Community Engagement: Engaging local communities living near the borders can foster a sense of ownership and encourage their participation in reporting suspicious activities.
29) Use of internet and social media by non-state actors for subversive activities is a major security concern. How have these been misused in the recent past? Suggest effective guidelines to curb the above threat. (200 words)
The use of the internet and social media by non-state actors for subversive activities has indeed become a major security concern.
Internet and social media misused by non-state actors in the recent past
In the recent past, several instances have been reported where non-state actors have used the internet and social media to further their nefarious agenda.
Internet and social media misused by non-state actors in the recent past
In the recent past, several instances have been reported where non-state actors have used the internet and social media to further their nefarious agenda.
- Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) used social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook and Telegram to recruit new members, spread propaganda and carry out cyber-attacks.
- Terrorist groups like Al-Qaeda and Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) have also been using the internet for propaganda and communication purposes.
- Stringent Cyber Laws: Governments need to formulate and implement stringent cyber laws that criminalize the misuse of the internet and social media for subversive activities.
- Collaboration with Internet Companies: Governments should collaborate with internet companies to ensure that their platforms are not used for subversive activities.
- Capacity Building: Governments should invest in building the capacity of law enforcement agencies to effectively track and investigate online activities of non-state actors.
- Public Awareness: Governments should launch public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the dangers of online radicalisation
2015
30) Human right activists constantly highlight the fact that the Armed forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 (AFSPA) is a draconian act leading to cases of human right abuses by security forces. What sections of AFSPA are opposed by the activists? Critically evaluate the requirement with reference to the view held by Apex Court. (200 words)
The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 (AFSPA) is a legislation that grants special powers to the armed forces in "disturbed areas" to maintain public order and combat insurgency.
Sections of AFSPA opposed by activists
Sections of AFSPA opposed by activists
- Section 4(a): This section grants special powers to armed forces personnel, such as the power to use force, arrest without warrant, and enter and search premises, in order to maintain public order.
- Section 4(b): It provides immunity to armed forces personnel from legal prosecution for their actions performed in "good faith" and "in the discharge of their duty."
- Section 6: Activists contend that this provision allows for a prolonged and arbitrary application of AFSPA, leading to human rights abuses even in areas that may not require such exceptional powers.
- Use of force: The court has emphasized that the use of force must be proportional to the situation and in accordance with the principles of necessity and proportionality.
- Impunity: The court has recognized the need to prevent impunity and ensure accountability for human rights abuses.
- Oversight mechanisms: The court has stressed the importance of establishing effective oversight mechanisms to ensure accountability and address grievances.
- The AFSPA is applied to an area only when the ordinary laws of the land are found to be inadequate to deal with the extraordinary situation perpetrated by insurgents spreading terror.
- Insurgent movements in India have more or less been proxy wars being waged against India by external actors and this necessitates the deployment of armed forces in a counter-insurgency role with enhanced legal protection.
- If AFSPA is repealed, as is being demanded, the army would have to be withdrawn from that state or area which will create a huge gap in the security grid and will give terrorists, be it in Kashmir and Manipur, the upper hand.
- Violates Human Rights: The act fails to protect and uphold human rights. The act reinforces a militarized approach to security which has proved to be not only inefficient but, also counterproductive in tackling security challenges. E.g.: alleged custodial rape and killings of the Thangjam Manorama by the Assam rifles in 2004.
- Misuse of Absolute Power: The absolute authority vested in the armed forces to shoot on sight based on mere suspicion and for an offence as basic as violating an order. Eg.: The power to shoot on sight violates the fundamental right to life,
- Violates Fundamental Rights: The power of arbitrary arrest and detention given to the armed forces goes against the fundamental right vested in Article 22, which provides safeguards for preventive and punitive detentions.
- Immunity against any Punitive Action: The greatest outrage against AFSPA is due to the immunity given to the armed forces. No prosecution, suit or another legal proceeding shall be instituted except with the previous sanction of the central government. This immunity which protects guards and also facilitates the armed forces to take unwarranted decisions at times is clearly questionable.
31) Religious indoctrination via social media has resulted in Indian youth joining the ISIS. What is ISIS and its mission? How can ISIS be dangerous to the internal security of our country? (200 words)
ISIS, also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria or the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), is a militant extremist group that emerged in the early 2000s. Its mission, as proclaimed by the group itself, is to establish a caliphate governed by a strict interpretation of Islamic law (Sharia) across a wide territory, with the ultimate goal of achieving global dominance and implementing its extremist ideology.
Impact of ISIS on India’s internal security
Impact of ISIS on India’s internal security
- Radicalization and Recruitment: The targeted indoctrination of Indian youth through social media has resulted in some joining the ranks of ISIS.
- Terrorist Attacks: The possibility of ISIS-inspired attacks within India can destabilize internal security and create fear and panic among the population.
- Recruitment of Local Support Networks: These networks serve as a breeding ground for local militant groups to align themselves with the ideology and methods of ISIS.
- Sectarian Tensions: In a diverse country like India, where inter-religious harmony is vital, the propagation of ISIS ideology can exacerbate sectarian tensions and lead to communal conflicts.
- Border Security: India shares borders with countries facing significant ISIS presence and conflict, such as Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- Intelligence Gathering and Sharing: Strengthen intelligence agencies to monitor and gather information on potential ISIS sympathizers, recruiters, and radicalized individuals.
- Counter Radicalization Programs: Implement community engagement and deradicalization programs to counter the appeal of ISIS ideology.
- Law Enforcement Capacity Building: Enhance the capabilities of law enforcement agencies to respond to emerging threats effectively. Provide specialized training to deal with terrorism-related situations and improve investigative techniques.
- Cyber security Measures: Upgrade cyber security infrastructure to thwart online radicalization and propaganda dissemination by ISIS and its sympathizers.
32) The persisting drives of the government for development of large industries in backward areas have resulted in isolating the tribal population and the farmers who face multiple displacements. With Malkangiri and Naxalbari foci, discuss the corrective strategies needed to win the Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) doctrine affected citizens back into mainstream of social and economic growth. (200 words)
Left-wing extremism (LWE), also known as Naxalism or Maoism in the Indian context, is a political ideology and movement that seeks to bring about radical social, economic, and political changes through armed struggle and revolutionary means.
Causes of Left-Wing Extremism in India
Causes of Left-Wing Extremism in India
- Social and Economic Inequities: Historical land-related injustices, lack of access to basic services, and socio-economic disparities have contributed to the emergence of left-wing extremism in marginalized communities.
- Grievances against the State: Perceived government neglect, corruption, and human rights violations have fuelled resentment and support for extremist ideologies.
- Forest and Land Rights: LWE often finds support among tribal communities fighting for their traditional land and forest rights against exploitation by external actors, including private companies.
- Weak Governance and Development deficit: Inadequate governance, lack of infrastructure, and slow development in remote areas have left local populations susceptible to extremist influence.
- Inclusive Development: Special attention should be given to infrastructure development, job creation, and skill development programs in these regions, providing sustainable livelihood opportunities for the local communities.
- Land and Forest Rights: Implementing and effectively enforcing the Forest Rights Act and other relevant laws can help safeguard their traditional rights over land and natural resources.
- Dialogue and Conflict Resolution: This dialogue should focus on addressing their concerns, understanding their grievances, and finding peaceful and negotiated solutions to long-standing issues.
- Good Governance and Accountability: Strengthening governance structures and improving the delivery of public services in LWE-affected areas is essential.
- Social Welfare and Human Rights Protection: Prioritizing social welfare programs, such as healthcare, education, and social security, can significantly improve the lives of LWE-affected citizens.
- Rehabilitation and Reintegration: Providing rehabilitation and reintegration programs for former LWE cadres and affected citizens can help them reintegrate into mainstream society.
33) Considering the threats cyberspace poses for the country, India needs a “Digital Armed Forces” to prevent crimes. Critically evaluate the National Cyber Security Policy, 2013 outlining the challenges perceived in its effective implementation. (200 words)
India faces a range of cyber security threats, including cyber-espionage, cyber-terrorism, ransomware attacks, data breaches, and phishing scams, which can disrupt critical infrastructure and compromise sensitive information.
Need of a “Digital Armed Forces” to prevent crimes
Challenges for effective implementation of the Policy
Need of a “Digital Armed Forces” to prevent crimes
- Growing Cyber Threats: In today's digital age, cyber threats have become more sophisticated and pervasive.
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: As more essential services and infrastructure are connected to the internet, protecting them from cyber-attacks becomes crucial.
- Enhanced Cyber Defence: A specialized Digital Armed Forces can develop and implement advanced cyber security measures, including intrusion detection systems, threat intelligence, and incident response capabilities, to proactively defend against cyber threats.
- Rapid Response to Cyber Incidents: Cyber-attacks can occur at any time and have rapid consequences. Having a dedicated Digital Armed Forces allows for a faster and more coordinated response to cyber incidents, mitigating the damage caused by cyber-attacks.
Challenges for effective implementation of the Policy
- Lack of Legal Framework: The absence of a dedicated legislation hampers effective implementation and enforcement of the policy.
- Coordination and Collaboration: Cybersecurity involves multiple stakeholders, including government agencies, law enforcement, private sector organizations, and citizens. Establishing robust mechanisms for information sharing, cooperation, and coordination between different entities can be a challenge.
- Capacity and Skill Gap: There is a significant gap in the availability of skilled professionals, cybersecurity experts, and law enforcement personnel trained in handling cybercrime investigations.
- Public Awareness and Participation: Challenges exist in effectively disseminating information, conducting awareness campaigns, and ensuring active participation from individuals and organizations.
- Emerging Technologies and Threat Landscape: The cybersecurity landscape is continuously evolving, with emerging technologies and new types of cyber threats emerging regularly.
2014
34) “The diverse nature of India as a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society is not immune to the impact of radicalism which is seen in her neighbourhood.” Discuss along with strategies to be adopted to counter this environment. (200 words)
India's diverse and pluralistic society, with a rich tapestry of religions, cultures, and ethnicities, indeed faces challenges in countering radicalism. The impact of radicalism in India's neighbourhood can also spill over and influence certain elements within the country.
Radical ideologies can permeate borders and have an impact on India's society, communal harmony, and national security. The reasons for this vulnerability can be attributed to factors such as ideological diffusion, cross-border movements, and the interconnected nature of extremist networks. It is important to acknowledge that radicalism does not represent the beliefs or actions of the majority but is often associated with a small, extremist segment within various communities.
Strategies to counter radicalism
Radical ideologies can permeate borders and have an impact on India's society, communal harmony, and national security. The reasons for this vulnerability can be attributed to factors such as ideological diffusion, cross-border movements, and the interconnected nature of extremist networks. It is important to acknowledge that radicalism does not represent the beliefs or actions of the majority but is often associated with a small, extremist segment within various communities.
Strategies to counter radicalism
- Promoting religious harmony and tolerance: Initiatives such as community outreach programs, cultural exchanges, and public education campaigns should be used to promote religious harmony and tolerance
- Addressing socio-economic disparities: The government must take steps to address these disparities through poverty reduction programs, education, and job creation.
- Strengthening law enforcement and intelligence agencies: India must invest in strengthening its law enforcement and intelligence agencies to better detect and prevent acts of terrorism.
- Addressing ideological differences: India must engage with extremist groups and individuals to better understand their grievances and motivations, and work towards finding common ground and promoting peaceful solutions.
35) International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above their territory. What do you understand by ‘airspace? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggest ways to contain the threat. (200 words)
Airspace refers to the portion of the atmosphere above a country's territory that is subject to its legal jurisdiction and control.
Implications of international civil aviation laws
Implications of international civil aviation laws
- Jurisdiction and Control: Countries have the authority to regulate and control the use of their airspace, including the operation of aircraft, air traffic control services, and the establishment of safety regulations.
- National Security: Countries can enforce security measures within their airspace to protect their sovereignty, territory, and national interests.
- Safety and Regulation: Countries are responsible for ensuring the safety of aircraft operating within their airspace.
- Airspace Incursions: Unauthorized entry or intrusion into a country's airspace by military aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), or civilian aircraft can lead to airspace violations and potential conflicts.
- Airspace Disputes: Overlapping claims or disputes over airspace between neighbouring countries can strain diplomatic relations and potentially escalate into conflicts.
- Cyber Threats: The increasing reliance on digital systems for air traffic management and communication introduces the risk of cyberattacks.
- Enhanced Surveillance and Monitoring
- Airspace Management Systems
- International Cybersecurity Cooperation
- Establish comprehensive and updated regulations
36)How does illegal transborder migration pose a threat to India’s security? Discuss the strategies to curb this, bringing out the factors which give impetus to such migration. (200 words)
Illegal transborder migration refers to the movement of individuals across international borders without proper authorization or documentation, violating the immigration laws of the destination country.
Illegal transborder migration poses a threat to India's security
Illegal transborder migration poses a threat to India's security
- National Security: Unregulated and unauthorized migration across borders can facilitate the infiltration of terrorists, criminals, and extremist elements into the country, posing a significant threat to national security.
- Socioeconomic Impact: Large-scale illegal migration can strain local resources, including jobs, housing, and healthcare, leading to social tensions and conflicts. It can also contribute to the exploitation of migrants and create economic disparities.
- Border Management Challenges: Illegal migration challenges effective border management efforts, making it difficult for authorities to control and regulate movement across borders.
- Trafficking and Organized Crime: Transborder migration routes are often exploited by human trafficking networks and organized crime groups.
- Economic Disparities: Economic disparities between countries or regions can push individuals to seek better opportunities and higher wages in more prosperous areas.
- Poverty and Unemployment: Poverty and lack of employment opportunities in certain regions may compel people to seek better livelihoods and economic prospects across borders.
- Social and Religious Persecution: People facing persecution based on their ethnicity, religion, or social group may choose to migrate to escape discrimination and violence.
- Political Instability and Conflict: Political instability, civil unrest, and armed conflicts in some countries force people to flee in search of safety and security in neighbouring or distant countries.
- Environmental Factors: Natural disasters, climate change, and environmental degradation can disrupt livelihoods and compel people to move to more habitable regions.
- Enhancing border infrastructure, surveillance systems, and patrolling to detect and prevent unauthorized crossings.
- Strengthening cooperation with neighbouring countries through information sharing, intelligence collaboration, joint border patrols, and extradition agreements.
- Implementing and enforcing robust immigration policies and laws to deter illegal migration.
- Improve intelligence gathering and sharing mechanisms among law enforcement agencies.
- Addressing the root causes of illegal migration by promoting regional development initiatives, poverty alleviation programs, and creating employment opportunities.
37) In 2012, the longitudinal marking for high-risk areas for piracy was moved from 65 degrees east to 78 degrees east in the Arabian Sea by the International Maritime Organization. What impact does this have on India’s maritime security concerns? (200 words)
International Maritime Organization moved the longitudinal marking for high-risk areas for piracy from 65 degrees east to 78 degrees east in the Arabian Sea
Impact of this move on India
Impact of this move on India
- Increased Coverage: This increased coverage directly affects India's maritime security as it has a long coastline along the Arabian Sea and is vulnerable to piracy threats.
- Expanded Operational Zone: The new marking extends the operational zone for counter-piracy operations by international naval forces, including those conducted by India. This allows for a more proactive approach in patrolling and safeguarding the extended high-risk area against piracy incidents.
- Enhanced Cooperation: It encourages joint patrols, information sharing, and coordination among navies and maritime security agencies to effectively address the piracy threat in the Arabian Sea.
- Improved Maritime Domain Awareness: The new marking necessitates an improvement in India's maritime domain awareness capabilities.
- Implications for Trade and Economy: Piracy incidents can disrupt maritime trade and affect the economy. The extension of the high-risk area highlights the importance of ensuring safe and secure maritime transportation for India's trade relations with other countries and the stability of its economy.
38) China and Pakistan have entered into an agreement for development of an economic corridor. What threat does this pose for India’s security? Critically examine. (200 words)
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a joint initiative between China and Pakistan to develop a network of roads, railways, and pipelines to transport oil and gas from Gwadar port in Pakistan to China’s north western region.
Challenges posed by CPEC for India’s security
Challenges posed by CPEC for India’s security
- Strategic Implications: The CPEC involves the construction of infrastructure and transportation networks connecting China's western region to the Pakistani port of Gwadar, providing China with a direct access route to the Arabian Sea. This deepens China's presence in the region and raises concerns about its strategic interests, potentially encircling India and impacting India's security dynamics.
- Territorial Integrity: The CPEC passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK), which is a disputed territory between India and Pakistan. India views this as a violation of its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Security Threats: The presence of Chinese military assets and increased maritime activities could have implications for India's maritime security in the Arabian Sea.
- Regional Power Shift: The growing China-Pakistan alliance and their deepening economic cooperation through the CPEC could potentially shift the regional power dynamics.
- Diplomacy and Dialogue: Engage in open and constructive dialogue with China and Pakistan to address concerns and potential issues related to CPEC.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensure transparency in the implementation of CPEC projects and the utilization of funds to avoid any perception of a hidden or unfair agenda.
- Focus on Mutual Benefits: Emphasize the mutual benefits of CPEC for all parties involved. Seek opportunities for win-win collaborations in trade, investment, and infrastructure development.
- Addressing Environmental Concerns: CPEC projects should adhere to sustainable and environmentally friendly practices to minimize ecological impacts.
2013
39) Money laundering poses a serious security threat to a country’s economic sovereignty. What is its significance for India and what steps are required to be taken to control this menace? (200 words)
India, being a growing economy with a large informal sector, is particularly vulnerable to money laundering activities. Money laundering in India is primarily associated with corruption, tax evasion, and illicit financing of terrorist activities.
Significance/impacts Money laundering for India
Significance/impacts Money laundering for India
- Economic Impact: Money laundering undermines a country's economic stability and hinders legitimate economic growth. It distorts markets, erodes investor confidence, and negatively affects financial institutions' integrity.
- Loss of Tax Revenue: Money laundering prevents the government from collecting taxes on illegal transactions, leading to a decrease in tax revenue, which could have been used for public welfare and development.
- Financial System Vulnerability: When illicit funds enter the formal financial system, it exposes financial institutions to reputational risks, potential legal actions, and regulatory sanctions. This, in turn, weakens the overall financial system's stability.
- Terrorist Financing: Money laundering facilitates terrorist financing by providing an avenue for terrorist organizations to move funds globally and support their activities, posing a direct security threat to the country.
- Organized Crime Proliferation: Money laundering enables organized crime syndicates to operate and expand their criminal activities by providing them with a means to legitimize their ill-gotten gains.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002: It provides for the prevention, detection, and prosecution of money laundering activities.
- Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) and the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI): To investigate and prosecute cases of money laundering.
- Comprehensive legal framework: for the confiscation and forfeiture of assets acquired through money laundering.
- Electronic payment systems: To reduce the use of cash transactions.
- Improving international cooperation: Cooperation with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and bilateral agreements with other countries.
40) What are social networking sites and what security implications do these sites present? (200 words)
Social networking sites are online platforms that allow individuals to connect with each other and share information, images, videos, and other content. Some of the popular social networking sites include Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and Snapchat.
Security implications of social networking sites
Security implications of social networking sites
- Privacy Concerns: Social networking sites collect and store vast amounts of personal information, which can be accessed by the platform and sometimes shared with third parties.
- Identity Theft: Cybercriminals may exploit social networking sites to gather personal information, such as birthdates, addresses, and email addresses, which can be used for identity theft. Phishing attacks and social engineering techniques may be employed to deceive users and obtain sensitive information.
- Cyberbullying and Harassment: Social networking sites can be used as platforms for cyberbullying, harassment, or online abuse.
- Malware and Phishing Attacks: Social networking sites can be targets for malware distribution and phishing attacks.
- Data Breaches: Social networking sites store vast amounts of user data, making them attractive targets for hackers.
- Reputation and Online Exposure: Inappropriate or compromising posts, photos, or comments can have long-lasting consequences on personal and professional reputations.
41) Cyber warfare is considered by some defence analysts to be a larger threat than even Al Qaeda or terrorism. What do you understand by Cyber warfare? Outline the cyber threats which India is vulnerable to and bring out the state of the country’s preparedness to deal with the same. (200 words)
Cyber warfare refers to the use of digital techniques and technologies to launch attacks on computer systems, networks, and infrastructures of an adversary, with the intention of causing damage, disruption, or espionage.
Significance of cyberwarfare over traditional terrorism
Significance of cyberwarfare over traditional terrorism
- Scale and Reach: It has a global reach and can be conducted remotely from anywhere in the world.
- Anonymity and Attribution: Cyber attackers can often conceal their identities and origins, making it challenging to attribute attacks to specific individuals or states.
- Speed and Agility: Cyber-attacks can be launched quickly and with little warning, catching defenders off guard. The speed and agility of cyber operations make it challenging to respond in real-time effectively.
- Disruption of Critical Services: Cyber warfare can disrupt vital services such as power grids, financial systems, communication networks, and transportation, causing widespread chaos and panic.
- Cyber espionage: Foreign intelligence agencies and cybercriminals may attempt to steal sensitive information from Indian government agencies, businesses, and individuals.
- Hacking and malware attacks: Hackers and cybercriminals may attempt to gain unauthorized access to computer systems and networks in order to steal data or cause damage.
- Cyber terrorism: Terrorist groups may attempt to launch cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power grids or transportation systems.
- Legal framework and cybersecurity initiatives: Information Technology Act, 2000, the National Cyber Security Coordinator's office and the Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) to address cyber threats and National Cyber Security Policy to enhance cybersecurity measures.
- Capacity building and skill development: Efforts are being made to develop cybersecurity expertise through initiatives like setting up cyber security centres of excellence and promoting cybersecurity education and training programs
- Cybersecurity infrastructure: National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) aims to protect critical infrastructure sectors from cyber-attacks.
42) Article 244 of the Indian Constitution relates to administration of schedules area and tribal areas. Analyse the impact of non-implementation of the provisions of the Fifth schedule on the growth of Left-Wing extremism (200 words).
Article 244 of the Indian Constitution relates to the administration of Scheduled Areas and Tribal Areas. The Fifth Schedule of the Constitution provides for the administration and control of Scheduled Areas, which are areas inhabited by tribal communities.
Impact of non-implementation of the provisions of the Fifth schedule on the growth of LWE
Impact of non-implementation of the provisions of the Fifth schedule on the growth of LWE
- Displacement and Alienation: The non-implementation of Fifth Schedule provisions has resulted in the displacement and alienation of tribal communities from their lands and resources. It results in the growth of Left-Wing extremism.
- Exploitation and Injustice: The lack of implementation of protective measures for tribal communities has led to the exploitation of their resources by external entities, including private companies and non-tribal settlers. It also leads to the growth of Left-Wing extremism.
- Economic Deprivation and Poverty: The non-implementation of provisions such as land reforms, agricultural support, and livelihood opportunities in tribal areas has resulted in economic deprivation and poverty, which results in the growth of Left-Wing extremism.
- Weakening of Traditional Institutions: The non-implementation of the Fifth Schedule provisions has weakened traditional tribal institutions and governance systems. This facilitated the growth of Left-Wing extremism.
43) How far are India’s internal security challenges linked with border management particularly in view of the long porous borders with most countries of South Asia and Myanmar? (200 words)
India's internal security challenges are indeed linked with border management, especially due to the long and porous borders it shares with several countries in South Asia and Myanmar.
India’s internal security challenges linked with border management
India’s internal security challenges linked with border management
- Infiltration and Illegal Activities: Porous borders provide opportunities for unauthorized entry of individuals, including militants, criminals, and illegal immigrants.
- Insurgent Groups and Safe Havens: Porous borders allow insurgent groups to establish safe havens and transit routes across international boundaries. This enables them to carry out attacks, recruit members, and engage in cross-border activities.
- Transnational Crimes and Networks: Porous borders facilitate the operations of transnational criminal networks engaged in activities like human trafficking, arms smuggling, drug trafficking, and counterfeit currency circulation.
- Illegal Trade and Economic Implications: Unregulated cross-border trade and smuggling impact the economy and disrupt legitimate business activities. The influx of cheap counterfeit goods and unauthorized trade can harm domestic industries, affect revenue collection, and create economic imbalances.
- Vulnerability to External Influence: Porous borders can make a country susceptible to external influences, including interference in internal affairs, radicalization, and the spread of extremist ideology
- Enhanced Border Surveillance and Technology: Deploy advanced surveillance technologies such as radar, drones, CCTV cameras, and sensor-based systems to monitor and secure the borders.
- Border Infrastructure Development: Improve physical infrastructure at border areas, including constructing roads, installing lighting systems, and establishing border outposts.
- Use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Employ UAVs for surveillance and reconnaissance purposes, enabling real-time monitoring of border areas and providing vital intelligence to security forces.
- Enhanced Coordination Among Agencies: Improve coordination among various security agencies, including the military, border security forces, customs, immigration, and intelligence agencies, to streamline border management efforts.
- Capacity Building and Training: Provide specialized training to security personnel to handle the challenges posed by the porous borders. Training should include border management, handling transnational crimes, and using modern surveillance equipment.


